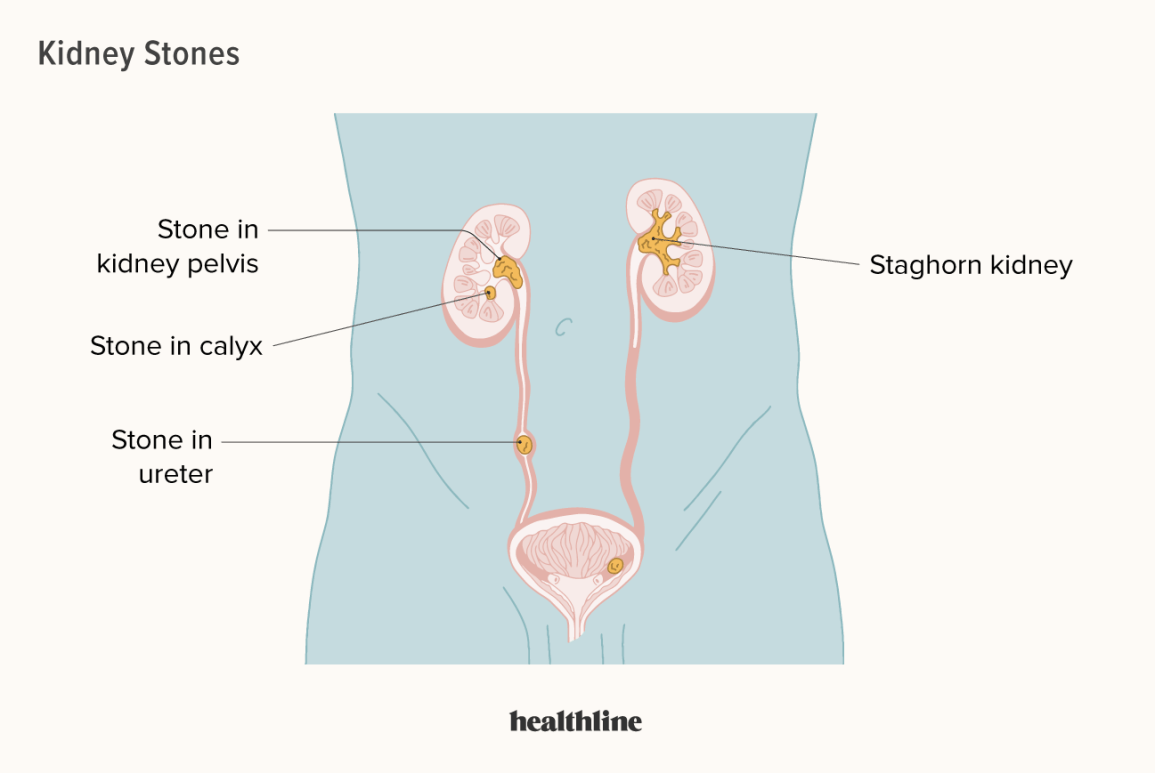
Kidney Stones
Chính Sách Vận Chuyển Và Đổi Trả Hàng
Miễn phí vận chuyển mọi đơn hàng từ 500K
- Phí ship mặc trong nước 50K
- Thời gian nhận hàng 2-3 ngày trong tuần
- Giao hàng hỏa tốc trong 24h
- Hoàn trả hàng trong 30 ngày nếu không hài lòng
Mô tả sản phẩm
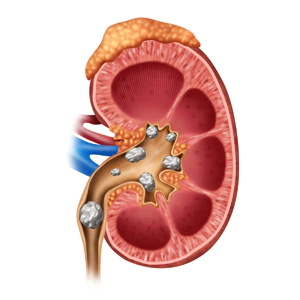
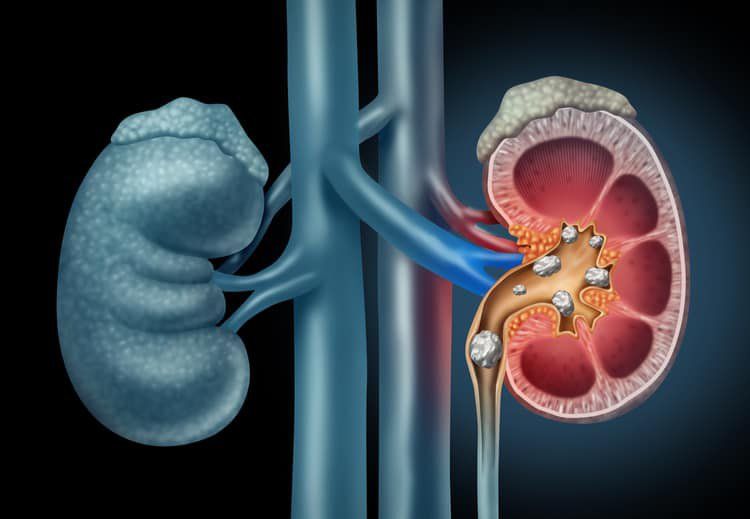
Kidney stones are hard, crystalline mineral and salt deposits that form inside your kidneys. They can cause significant pain and discomfort, and if left untreated, can lead to serious complications.
What are Kidney Stones?
Formation and Composition
Kidney stones form when the urine becomes supersaturated with substances like calcium, oxalate, uric acid, cystine, or struvite. These substances then crystallize and clump together, growing larger over time. The exact cause of kidney stone formation varies, but factors like dehydration, diet, certain medical conditions, and genetics all play a role.Types of Kidney Stones
There are several types of kidney stones, each with a different chemical composition and potential risk factors:- Calcium stones: The most common type, often composed of calcium oxalate.
- Uric acid stones: Form in individuals with high uric acid levels, often associated with a high-purine diet.
- Struvite stones: Often related to urinary tract infections.
- Cystine stones: A rare type caused by a genetic disorder affecting cystine metabolism.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Pain and Discomfort
The most prominent symptom of kidney stones is intense pain, often described as a sharp, cramping pain in the flank (side) or lower back. This pain can radiate to the groin, abdomen, or inner thigh. The pain can come and go in waves.Other Symptoms
Besides pain, other symptoms can include:- Frequent urination
- Pink, red, or brown urine
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills (if infection is present)
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis
Diagnosing kidney stones usually involves a physical exam, medical history review, and imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds. Urine tests may also be performed to analyze the stone composition.Treatment
Treatment options depend on the size, location, and symptoms of the kidney stone. Small stones may pass on their own with increased fluid intake and pain medication. Larger stones may require medical intervention, including lithotripsy (using shock waves to break up the stone), ureteroscopy (removing the stone with a scope), or surgery.Prevention of Kidney Stones
Hydration
Drinking plenty of water is crucial for preventing kidney stones. It helps dilute the urine and reduces the concentration of stone-forming substances.Diet
Dietary changes can also help. Limiting sodium intake, animal protein, and oxalate-rich foods can be beneficial. Consult a doctor or registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice.Xem thêm: tác dụng của 3b
Xem thêm: axit axetic tác dụng với na2co3
Xem thêm: al + hcl hiện tượng
Sản phẩm hữu ích: trẻ trâu tiếng anh la gì