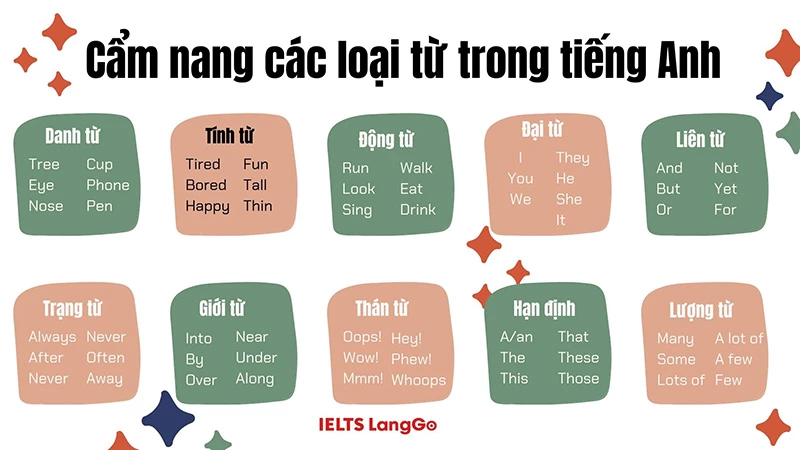
Types of English Words
Chính Sách Vận Chuyển Và Đổi Trả Hàng
Miễn phí vận chuyển mọi đơn hàng từ 500K
- Phí ship mặc trong nước 50K
- Thời gian nhận hàng 2-3 ngày trong tuần
- Giao hàng hỏa tốc trong 24h
- Hoàn trả hàng trong 30 ngày nếu không hài lòng
Mô tả sản phẩm
English words are categorized in several ways, depending on their grammatical function and meaning. The main types include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, and determiners. Understanding these categories is crucial for mastering English grammar and vocabulary.
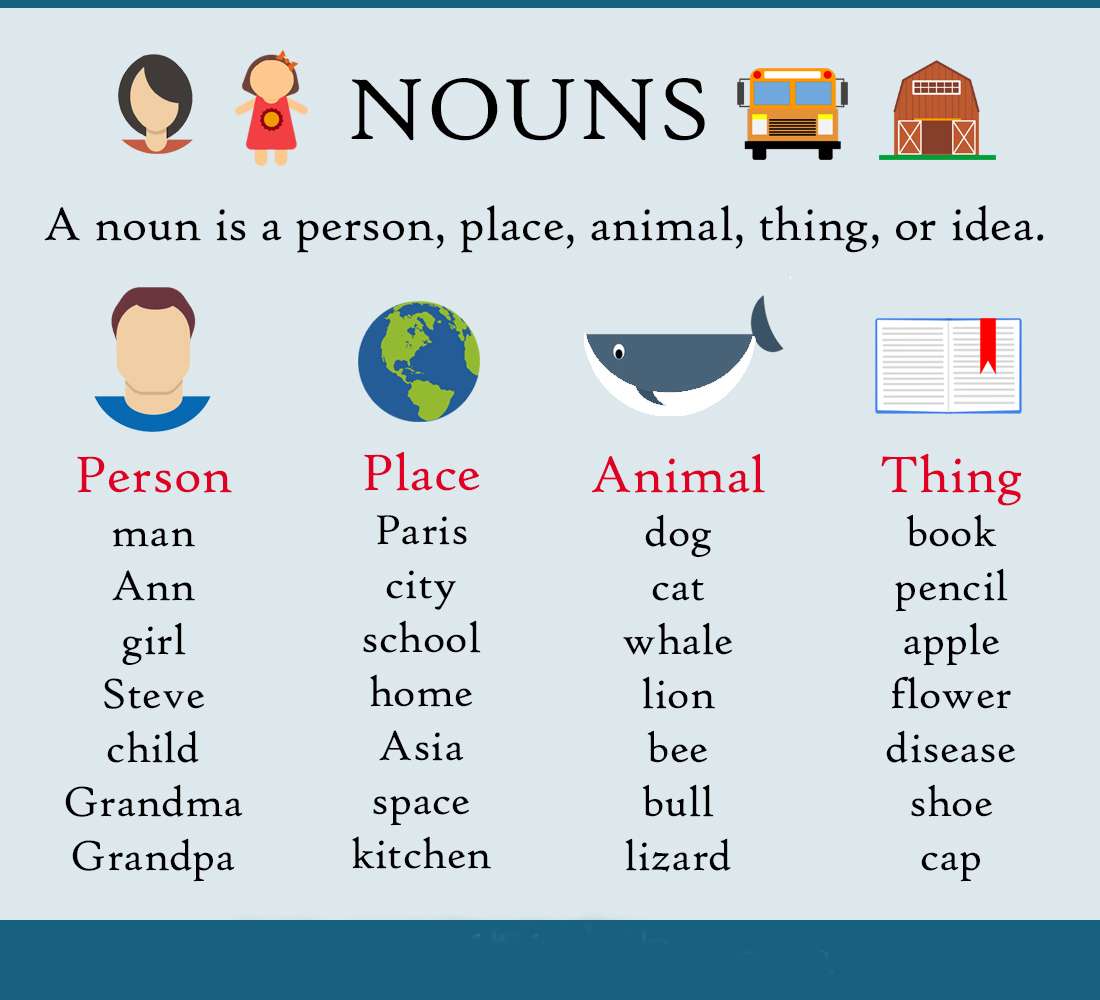
Nouns
Types of Nouns
Nouns represent people, places, things, or ideas. They can be further categorized into common nouns (e.g., dog, house, city), proper nouns (e.g., Fido, London, Microsoft), concrete nouns (things you can touch), abstract nouns (ideas, concepts), collective nouns (groups, e.g., team, flock), countable nouns (can be counted, e.g., apples, books), and uncountable nouns (cannot be counted, e.g., water, sugar).
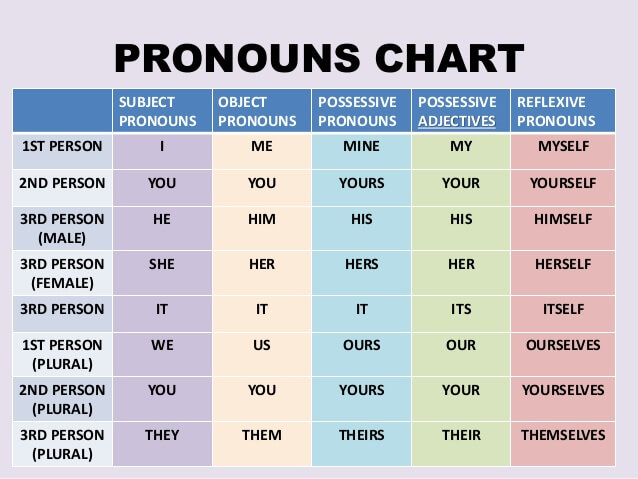
Pronouns
Examples of Pronouns
Pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition. They include personal pronouns (I, you, he, she, it, we, they), possessive pronouns (mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs), reflexive pronouns (myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves), demonstrative pronouns (this, that, these, those), interrogative pronouns (who, whom, whose, which, what), relative pronouns (who, whom, whose, which, that), and indefinite pronouns (someone, anyone, everyone, no one, somebody, anybody, everybody, nobody, something, anything, everything, nothing).
Verbs
Verb Tenses and Aspects
Verbs show action or state of being. They are conjugated to indicate tense (past, present, future), aspect (simple, progressive, perfect, perfect progressive), mood (indicative, imperative, subjunctive), and voice (active, passive). Understanding verb conjugation is key to constructing grammatically correct sentences.
Adjectives
Descriptive Adjectives
Adjectives describe or modify nouns and pronouns. They answer questions like "what kind," "which one," or "how many." Examples include: big, small, red, happy, intelligent.
Adverbs
Adverbial Modifiers
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They often end in "-ly" (e.g., quickly, happily, sadly) but not always. They answer questions like "how," "when," "where," or "to what extent."
Prepositions
Prepositional Phrases
Prepositions show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence. They indicate location, direction, time, or manner. Examples include: on, in, at, above, below, beside, before, after, with, without.
Conjunctions
Coordinating and Subordinating Conjunctions
Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses. Coordinating conjunctions (and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet) join elements of equal grammatical rank. Subordinating conjunctions (because, although, since, if, while) introduce dependent clauses.
Interjections
Expressive Words
Interjections express strong emotion. They are often followed by an exclamation point. Examples include: Wow!, Ouch!, Oh no!, Hooray!
Determiners
Articles and Other Determiners
Determiners introduce nouns and specify their reference. They include articles (a, an, the), possessive determiners (my, your, his, her, its, our, their), demonstrative determiners (this, that, these, those), quantifiers (some, any, many, few, much, little), and numerals (one, two, three).
Sản phẩm hữu ích: think through là gì
Xem thêm: đồng nghĩa với kết quả
Sản phẩm liên quan: tìm hai số có tổng